Sources




We are the leading company in the storage of mesenchymal stem cells from different sources of the body.
We carry out a very simple process in which we collect the mesenchymal stem cells, with which we will work so that in the future they can have them, either to preserve the health of yourself or your direct family.







Cd. Mex: 5202-9828
Mty: (+52 81) 8311 1111
(+52 1) 81 8065 3713
Av.Cordillera de los Andes 115,
Lomas de Chapultepec, Miguel Hidalgo
Ciudad de México, Mex.

Also known as core cells (derived from the English stem cells) are defined as undifferentiated cells, capable of making identical copies of themselves. Stem cells can be differentiated when required in various cells of the body with specific functions (heart, liver, kidney, pancreas, etc.).
They are cells that are found in different areas of the body (dental pulp, adipose tissue, placenta and umbilical cord tissue) and can be differentiated into organs and tissues of the body.
It is considered that mesenchymal stem cells can be used in the regeneration of organs and tissues of our body, for example: bone, cartilage, ligament, muscle, tendons, skin, insulin-producing cells, cardiac cells, neural cells, retina cells, dental tissues, among others. They can be used in the treatment of diseases such as:
• Diabetes type 1
• Myocardial infraction
• Parkinson
• Alzheimer
• Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
• Spinal cord injuries
• Brain injuries caused by vascular events
• Diabetic foot
There are several protocols that are currently being carried out in Mexico, which are in the process of authorization for their clinical application. Mesenchymal cells obtained from other parts of the body have already been used with great success in combination with hematopoietic cells in bone marrow transplants, reducing side effects and the use of immunosuppressants.
Dental nerve or dental pulp
Adipose tissue
Placenta
Umbilical cord tissue
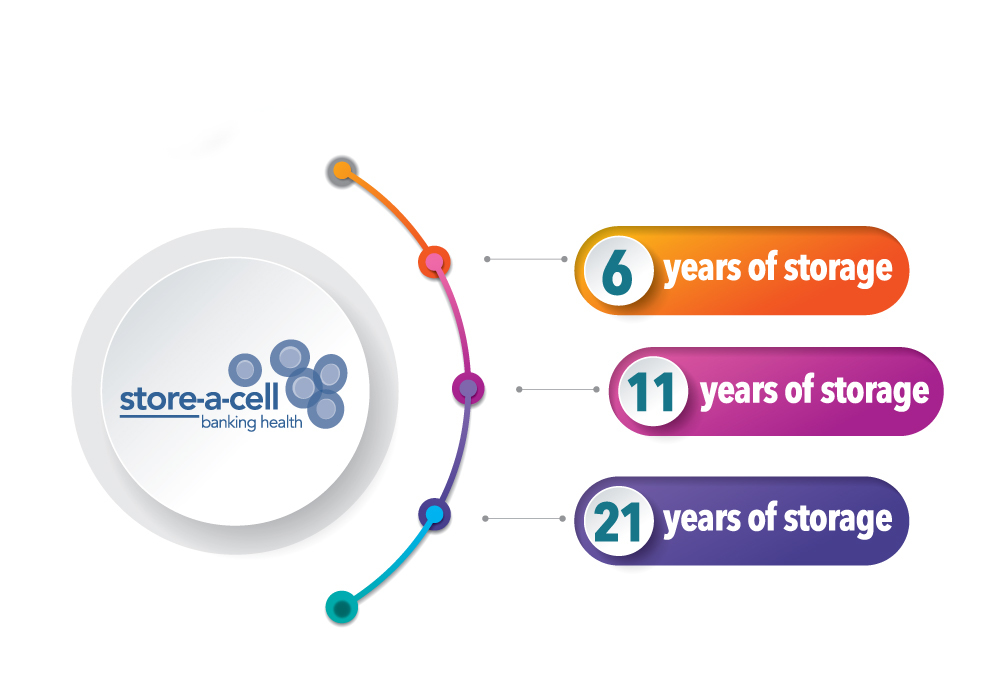
After the cryopreservation process, the biological activity stops; as a result, cells that are processed in an appropriate manner can be stored almost indefinitely. Human cells have effectively been stored for up to 50 years.
Although there is no age limit to save your cells, the younger the cells, the greater the chances of success in the process and the better quality of the same.
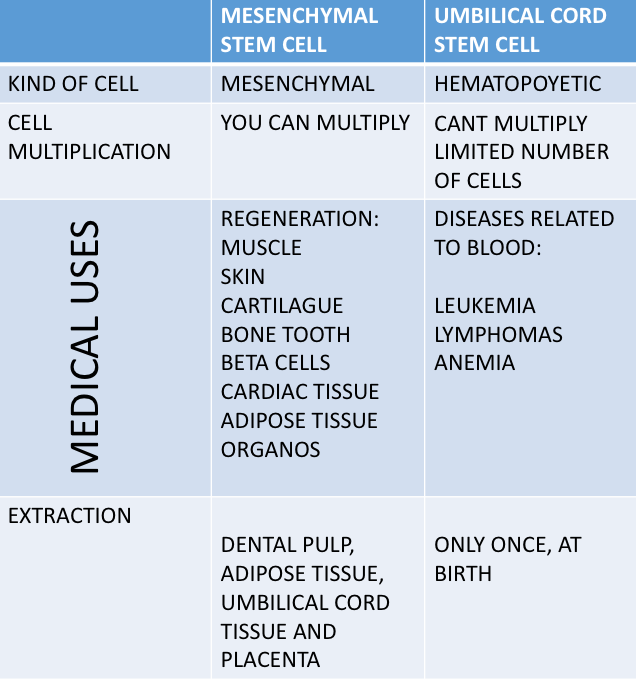
It is important to note that some do not replace the others but can be supplemented. In fact, they are used together in bone marrow transplants where mesenchymal cells efficiently modulate the response of the immune system, favoring the acceptance of hematopoietic (umbilical cord) cell transplantation.
The laboratory in which the Store a Cell processes are carried out has a license from Cofepris authorized for the disposal of organs, tissues and cells for therapeutic purposes in the form of progenitor cell bank. The preservation of the cells is guaranteed for the contracted time, even if the company stops offering this service. The cells are deposited in four different containers as an additional guarantee. Our laboratory has validated its process of isolation, transport, culture and cryopreservation of dental stem cells together with the Institute of Biomedical Research of UNAM, with whom an official joint research agreement has been established. Our laboratory has validated its process of isolation, transport, culture and cryopreservation of dental stem cells together with the Institute of Biomedical Research of UNAM, with whom an official joint research agreement has been established.
For more information, call:01 55-5202-9828; or send an email to servicioaclientes@storeacell.com; or, if you like, a representative can visit you in your home or office.

The human body is surprising, so much it possesses the source of its own health and wellness inside: Mesenchymal Stem Cells.
Recent scientific breakthroughs have allowed to harvest these stem cells from our body and store them so they can be available whenever we need them.
One of the sources is the placenta tissue. These cells are collected after delivery through a non-invasive process that does not involve harm to the new born baby or the mother.1,2,5
These cells have a high capacity to reproduce (multiply) so we can obtain a large number of them and maintain their availability for several years.3,4
Mesenchymal stem cells have the capacity to differentiate into other cells of the body giving them the potential to regenerate tissues and organs like:3,5,6
Placenta tissue mesenchymal stem cells have been studied and considered for their use as therapeutic alternatives in:3,4,6
References:
1. Anelise Bergmann Araujo 1,2, Gabrielle Días Salton 1, Juliana Monteiro Furlan 1, Natália Scheider 2, Melissa Helena Angel 1, Álvaro Macedo Laureano 3, Lúcia Silla 3, Eduardo Pandolfi Passos 2 and Ana Helena Paz 2. Comparison of human mesenchymal stromal cells from four neonatal tissues: Amniotic membrane, chorionic membrane, placental decidua and umbilical cord (2017). Cytotherapy, Vol 19: 577–585
2. Naimisha Beeravolu1,2, Christina McKee1,2, Ali Alamri1,2, Sasha Mikhael3, Christina Brown1,2, Mick Perez-Cruet2,4, G. Rasul Chaudhry1,2. Isolation and Characterization of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Human Umbilical Cord and Fetal Placenta (2017). Journal of Visualized Experiments (122), e55224.
3. Alessandra Fierabracci†, Lorenza Lazzari, Maurizio Muraca & Ornella Parolini. How far are we from the clinical use of placental derived mesenchymal stem cells? (2014). Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy, Vol 15(5):613-617.
4. Gary Brooke,1* Tony Rossetti,1* Rebecca Pelekanos,1 Nina Ilic,2 Patricia Murray,1 Sonia Hancock,1 Vicki Antonenas, 3 Gillian Huang,3 David Gottlieb, 3 Ken Bradstock3 and Kerry Atkinson. Manufacturing of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells for clinical trials (2008). British Journal of Haematology, Vol 144, 571–579.
5. Maira S Oliveira, João B Barreto-Filho. Placental-derived stem cells: Culture, differentiation and challenges (2015). World Journal Stem Cells, Vol 7(4): 769-775.
6. Chiho Ikebe and Ken Suzuki. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Regenerative Therapy: Optimization of Cell Preparation Protocols. Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International, Vol 2014; 11.

The human body is surprising, so much it possesses the source of its own health and wellness inside: Mesenchymal Stem Cells.
Recent scientific breakthroughs have allowed to harvest these stem cells from our body and store them so they can be available whenever we need them.
One of the sources is the umbilical cord tissue. These cells are collected after delivery through a non-invasive process that does not involve harm to the new born baby or the mother.1,2
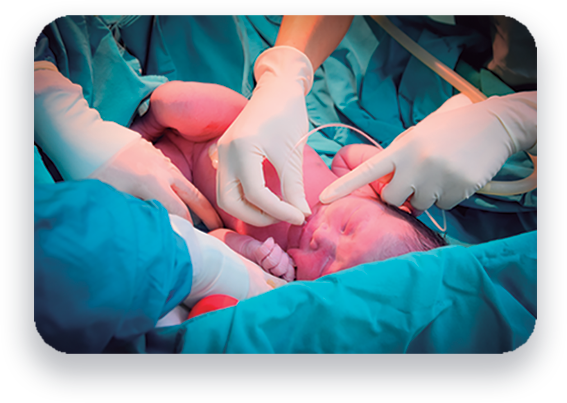
These cells have a high capacity to reproduce (multiply) so we can obtain a large number of them and maintain their availability for several years.1,2
Umbilical Cord mesenchymal stem cells have the capacity to differentiate into other cells of the body giving them the potential to regenerate tissues and organs like:2,3,4
Umbilical Cord mesenchymal stem cells have been studied and considered for their use as therapeutic alternatives in:1,3,4
References:
1. Alicja Zajdel*, Magdalena Kałucka, Edyta Kokoszka-Mikołaj and Adam Wilczok. Osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue and Wharton’s jelly of the umbilical cord (2017). Acta Biochimica Polonica, Vol. 64, 2: 365–369.
2. Chun Chen 1, 2, Zhiguo Qu3, Xiaoguang Yin2, Chunyu Shang 1, Qiang Ao4, YongQuan Gu 5 and Ying Liu 2, 6. Efficacy of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A three-year follow-up study (2016). Molecular Medicine Reports Vol 14: 4209-4215.
3. Chiho Ikebe and Ken Suzuki. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Regenerative Therapy: Optimization of Cell Preparation Protocols. Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International, Vol 2014; 11.
4. Christopher D. Phillips, Pornpatcharin Wongsaisri, Thein Htut and Terry Grossman. Purified umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cell treatment in a case of systemic lupus erythematosus (2017). Phillips et al. Clinical and Translational Medicine; 6:31.

The human body is surprising, so much it possesses the source of its own health and wellness inside: Mesenchymal Stem Cells.
Recent scientific breakthroughs have allowed to harvest these stem cells from our body and store them so they can be available whenever we need them.
One of the sources is the dental pulp. These cells can be collected in two ways:1

These cells have a high capacity to reproduce (multiply) so we can obtain a large number of them and maintain their availability for several years.1,2
Mesenchymal stem cells have the capacity to differentiate into other cells of the body giving them the potential to regenerate tissues and organs like:1
Dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells have been studied and considered for their use as therapeutic alternatives in:1,2
References:
1. Athina Bakopoulou and Imad About. Stem Cells of Dental Origin: Current Research Trends and Key Milestones towards Clinical Application (2016). Hindawi Publishing Corporation Stem Cells International, Vol 2016: 20.
2. Chiho Ikebe and Ken Suzuki. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Regenerative Therapy: Optimization of Cell Preparation Protocols. Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International, Vol 2014; 11.

The human body is surprising, so much it possesses the source of its own health and wellness inside: Mesenchymal Stem Cells.
Recent scientific breakthroughs have allowed to harvest these stem cells from our body and store them so they can be available whenever we need them.
One of the sources is the adipose tissue. These cells can be collected in two ways:1
These cells have a high capacity to reproduce (multiply) so we can obtain a large number of them and maintain their availability for several years.2,4
Mesenchymal stem cells have the capacity to differentiate into other cells of the body giving them the potential to regenerate tissues and organs like:1,2,3,4
Adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells have been studied and considered for their use as therapeutic alternatives in:2,3,4
References:
1. Christopher R. Fellows 1, CsabaMatta1, 2, RozaZakany2, IlyasM.Khan3 and Ali Mobasheri1. Adipose, Bone Marrow and Synovial Joint-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for cartilage repair (2016). Frontiers in Genetics, Vol 7: 20.
2. Louis Casteilla, Valérie Planat-Benard, Patrick Laharrague, Béatrice Cousin. Adipose-derived stromal cells: Their identity and uses in clinical trials, an update (2011). World J Stem Cells, Vol 26; 3(4): 25-33.
3. Yan Xu,1,2 Shilei Guo,1,2 CuiWei,1 Honglan Li,1 Lei Chen,1 Chang Yin,1 and Chuansen Zhang2. The Comparison of Adipose Stem Cell and Placental Stem Cell in Secretion Characteristics and in Facial Antiaging (2016). Hindawi Publishing Corporation Stem Cells International, Vol 2016: 14.
4. Chiho Ikebe and Ken Suzuki. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Regenerative Therapy: Optimization of Cell Preparation Protocols. Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International, Vol 2014; 11.